Ethics and Professional Standards
Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct
Guidance for Standards I-VII
Standards I - Professionalism
A. Knowledge of the Law
eg. Applicable law - report violation is not compelled unless such disclose is mandatory under applicable law
B. Independence and Objectivity
eg. Travel funding
eg. allocate shares in over-subscribed IPOs to personal account of investment managers
eg. pressure on sell-side analyst by buy-side clients
C. Misrepresentation
eg. Verify outside information
eg. Plagiarism
eg. Work completed for employer
the firm can use ex-employee's prior analysis without providing attribution
eg. prohibit assurances on an investment
D. Misconduct
eg. background check on prospective employers
eg. list of violations and assoc. disciplinary actions
Standards II - Integrity of Capital Markets
A. Material non-public information
eg. Non-public info can be used for conducting due diligence, cannot be used to trade securities of the firm
eg. info disseminated to select group of investors is nonpublic, not necessary to wait for slowest method of delivery
eg. Mosaic theory
can use mosaic info in analyst research report, the investment research reports not required to make public
eg. investment research reports
no need to make respected analyst report work of material non public info
eg. Firewall elements
eg. Source of Information
eg. A prohibition on all types of proprietary activity when a firm has possession of material nonpublic information is not appropriate.
proprietary trading procedures, firm acts as market maker can continue to trade
eg. CFA member/candidate should encourage the issuing company to make the information public. CFA member/candidate, however, is under no obligation to disseminate the information himself.
B. Market Manipulation
Standards III - Duties to Clients
A. Loyalty, Prudence, Care
eg. soft commission policies
eg. proxy voting policies
B. Fair Dealing
eg. treat all clients fairly when disseminate investment recommendation or taking investment action. not equally
allocate IPOs on pro-rata basis to all suitable clients
trade allocation procedures must be fair/equitable
eg. different level of service should not be offered to clients selectively
the different service level should be disclosed to clients
eg. members may provide more personalised service to clients for a premium fee
C. Suitability
eg. understand client risk profile
D. Performance Presentation
eg. consider the knowledge of audience to whom the presentation is addressed
E. Preservation of Confidentiality
eg. members and candidates must keep client info confidential unless client permits disclosure
Standards IV - Duties to Employers
A. Loyalty
B. Additional Compensation Arrangements
eg. disclose other benefits from third parties
C. Responsibilities of Supervisors
Standards V - Investment Analysis, Recommendations and Actions
A. Diligent and Reasonable Basis
B. Communication with Clients and Prospective Clients
C. Record Retention
eg. up to 7 years
Standards VI - Conflicts of Interest
A. Disclosure of Conflicts
B. Priority of Transactions
eg. personal trading secondary to trading for clients
C. Referral Fees
Standards VII - Responsibilities as a CFA institute member or candidate
A. Conduct as members and candidates in the cfa program
B. Reference to cfa institute, the cfa designation and the cfa program
Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS)
firms must meet all requirements set forth in the GIPS standards, and cannot claim partial compliance
third party verification enhances the credibility of the GIPS compliance
Quantitative Methods
Time value of money
FV = PV(1+r) - single period
FV = PV(1+r)
n - any number of periods
FV = PVe
rn - continuous compounding
effective annual rate
ear = (1 + period rate)
n -1
n: number of compounding period in a year
ear = e
rn -1 , for continuous compounding
annuity - finite perpetuity - infinite
ordinary annuity - first cash flow one period from now
annuity due - first cash flow happens immediately (t=0)
Annuity formula
FV = A[(1+r)
n-1]/r
PV = A[1-(1+r)
-n]/r
Perpetuity formula
PV = A/r
Discounted Cash flow Applications
bank discount basis (for T-Bill)
D = F * R
bd * t/360
F: face value
D: dollar discount difference between face value of T-Bill and price
t: remaining days to maturity
holding period yield
hpy = (P
1 - P
0 +D
1) / P
0
effective annual yield
eay = (1 + hpy)
365/t -1
money market yield
r
mm = hpy * 360/t
bond equivalent yield: double the semiannual ytm
(annual percentage rate)
time weighted return - use geometric mean
return = [(1+hpy
1)(1+hpy
2)(1+hpy
3)]
1/3 - 1
hpy1 : hpy for year 1
Statistics
statistical inference: make estimates about a larger group from a smaller group that is actually observed
sample statistic: a statistic computed from a sample
measurement scales:
nominal scales: categorise data, no rank
ordinal scales: sort and order data
interval scales: ranking data, differences between scale are equal
ratio scales: have a true zero point as the origin
median divides a distribution in half
quartiles into quarters
quintiles into fifths
percentiles into hundredths
mean absolute deviation =
Σni=1 | x
i - x̄ | / (n)
population variance =
Σni=1 (x
i - x̄)
2 / (n)
sample variance =
Σni=1 (x
i - x̄)
2 / (n-1)
coefficient of variation : CV =
s/x̄
sample skewness: positively skewed, negatively skewed
lognormal distribution is skewed to the right (positively skewed)
kurtosis: shows the probability of extreme outcomes
shows peakness of a distribution
Probability
Empirical probability: based on historical data and observation
Subjective probability: based on subjective judgement
A priori probability: based on logical analysis
Conditional Probability
P(A|B) = P(AB) | P(B)
Joint Probability
P(AB) = P(A|B)P(B)
P(AB) = P(BA)
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB)
Independent Events
P(AB) = P(A)P(B)
P(A|B) = P(A) P(B|A) = P(B)
Total Probability Rule
P(A) = P(AS) + P(AS
C)
P(A) = P(AS
1) + P(AS
2) + ... + P(AS
n)
P(A) is mutually exclusive and exhaustive
Baye's formula
using the occurrence of event to infer the probability of the scenarios generating it
update probability based on new info
P(A) = P(B|C)/P(B) * P(C)
Counting
labeling problem: n! / n1!n2! n3! .... nk!
combination: nCr = n!/(n-r)!r!
permutation: nPr = n!/(n-r)!
Odds:
odds of E = P(E)/[1 - P(E)]
odds against E = [1 - P(E)]/P(E)
Probability Distributions
Discrete random variable -> probability function
Continuous random variable -> probability density function
Binomial probability
p(x) = n!/(n-x)!x! * p
x(1-p)
n-x
Binomial distribution
X ~ B(n,p)
Normal distribution: most used probability density function, kurtosis of 3
X ~ N(
μ,
σ2)
Standard normal distribution (μ = 0, σ= 1)
standardizing a RV X : Z = (x -μ)/σ standard normal RV, Z(0,1)
Mean variance analysis
SFRatio = [E(Rp) - R
L] / σ
p (safety first ratio)
R
L - safety level
Coefficient of variation , CV = S/x̄
Monte Carlo Simulation
generate large number of random samples from specific probability distribution to represent the risk
Sampling and Estimation
Sampling methods:
- simple random sampling
- systematic sampling: The sampling starts by selecting an element from the ordered sampling frame at random, and then every kth element in the frame is selected
- stratified sampling: the process of dividing members of the population into homogeneous subgroups before sampling
distribution of sample mean: central limit theorem
population (μ, σ
2) of any distribution
sample, mean x̄ , (μ,
σ2/n) when sample size is large , n> 30
approximate normal distribution
standard error: Sx = S/ √n
σx =
σ/√n
Confidence Interval
given probability 1-α , degree of confidence that interval contains the parameter is 100(1-α)%
x̄ ± Z
α/2 σ/√n --> 100(1-α)% (confidence interval for population mean)
Z
α/2 -- standard normal distribution
90% - Z
0.05 = 1.65
95% - Z
0.025 = 1.96
99% - Z
0.005 = 2.58
x̄ ± Z
α/2 σ/√n (population variance is unknown, large sample size)
x̄ ± t
α/2 σ/√n (population variance is unknown, large sample size or small sample size but population is normally distributed)
Data mining bias (data snooping bias): finding models by repeatedly searching for patterns
Sample selection bias : survivorship bias
look ahead bias:
time period bias: time period used makes data time period specific
Hypothesis Testing
1. stating the hypothesis
null hypothesis, H
0, the hypothesis to be tested, H
0 is considered true unless evidence proves it to be false
alternative hypothesis, H
a, the hypothesis accepted when H
0 is rejected
two sided hypothesis
H
0 : θ=θ
0
H
a : θ
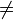
θ
0
one sided hypothesis
H
0 : θ

θ
0
H
a : θ
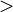
θ
0
2. define test statistics
x̄ - μ
------------
s/√n
choose test distribution: t-test
Z-test
X
2 test
F-test
3. specify the significance level
reflect how much sample evidence to reject H
0
reject false H
0
reject true H
0 -- type I error
do not reject false H
0 -- type II error
do not reject true H
0
4. state the decision rule
statistically significant ----> reject H
0
not statistically significant ----> do not reject H
0
eg. two sided test, 0.05 significant level, H
0 : θ=θ
0
Z
0.025 = 1.96 , Z
-0.025 = -1.96
Z < -1.96 or Z > 1.96 ---> reject H
0
eg. one sided test, 0.05 significant level, H
0 : θ

θ
0
Z
0.05 < 1.645 ,
Z > 1.645 ---> reject H
0
5. collect data, calculate test statistic
6. make statistical decision
7. make investment decision
p-value, smallest level of significant that H
0 can be rejected
p-value < sig. level --> reject H
0
p-value close to zero, H
0 should be rejected
single mean : t-test, Z-test
x̄ - μ
-------------
s/√n (n-1) df
difference between means: t-test
single variance: X
2-test
(n - 1) s2
X
2= -----------------
σ2 (n-1) df
difference between variance: F-test
s12 (n1-1) df1
F= -------------
s22 (n2-1) df2
Technical Analysis
head and shoulders: price target = neckline - ( head - neckline)
inverse head and shoulders: price target = neckline + (neckline - head)
moving average:
golden cross: short term moving average cross underneath a long term moving average
death cross: short term moving average cross above a long term moving average
bollinger bands: upper boundary band, lower boundary band
momentum indicators:
momentum oscillators: overbought, oversold
M = V/Vx * 100 V - last closing price
Vx - closed price x days ago
M = (V - Vx) * 100
relative strength index
stochastic oscillator :
> 70 overbought
< 30 oversold
moving average convergence/divergence (MACD)
difference between short term and long term moving average of price
flow of funds indicators
arms index (TRIN) = advanced number / declined number
------------------------------------------------
advanced volume / declined volume
Kondratieff wave: (K wave)
54 year economic cycle
5 up waves, impulse wave
3 down waves, corrective wave
1.618 golden ratio -> fibonacci ratio
relationship among wave heights is fibonacci ratio








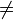 θ0
θ0 θ0
θ0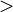 θ0
θ0